Free Preview
Guest writer Anand Khatri introduces several open-source investing ideas.
This article appears from guest contributor Anand Khatri. Anand is the founder of Stockscurrent and is a long-time friend of 7investing.
In the world of technology, you might have encountered the term “open-source software.” It refers to software programs developed collaboratively by a community of developers worldwide. The primary goal is to solve specific problems and create a solution that can benefit everyone without cost. This concept has been around for 50 years and continues to be a powerful force in technology. Although many successful companies have been built upon open-source solutions, the question remains: how can these companies make money or sustain themselves financially with open-source solution offerings?
Companies specializing in creating open-source software face the challenge of generating revenue from licensed software free of charge. To overcome this challenge, they employ various business models. These models are based on the assumption that users of open-source technologies are willing to purchase additional software features under proprietary licenses or other services that complement the open-source software that is core to the business. These extra services may include enterprise-grade features, uptime guarantees through a service-level agreement, performance and efficiency gains, legal protection, or professional support/training/consulting. These services are typically associated with proprietary software applications.
That’s great, but do you know which companies executed these models successfully and for profit? I will introduce two companies that performed exceptionally well, and one is on its way.
Red Hat
Red Hat (now part of IBM (NYSE: IBM)) is an American software company headquartered in North Carolina that offers open-source software products to enterprises. Established in 1993, Red Hat offers a wide range of products.
Red Hat is widely known for its enterprise operating system, Red Hat Enterprise Linux. In addition, Red Hat acquired the open-source enterprise middleware vendor JBoss and now offers Red Hat Virtualization (RHV), an enterprise virtualization product. The company provides a range of products and services, including storage, operating system platforms, middleware, applications, management products, support, training, and consulting services.
Red Hat is actively involved in creating, maintaining, and contributing to numerous free software projects. The company has obtained several proprietary software product codebases through corporate mergers and acquisitions and has subsequently released this software under open-source licenses. As of March 2016, Red Hat ranked as the second largest corporate contributor to the Linux kernel version 4.14, following Intel.
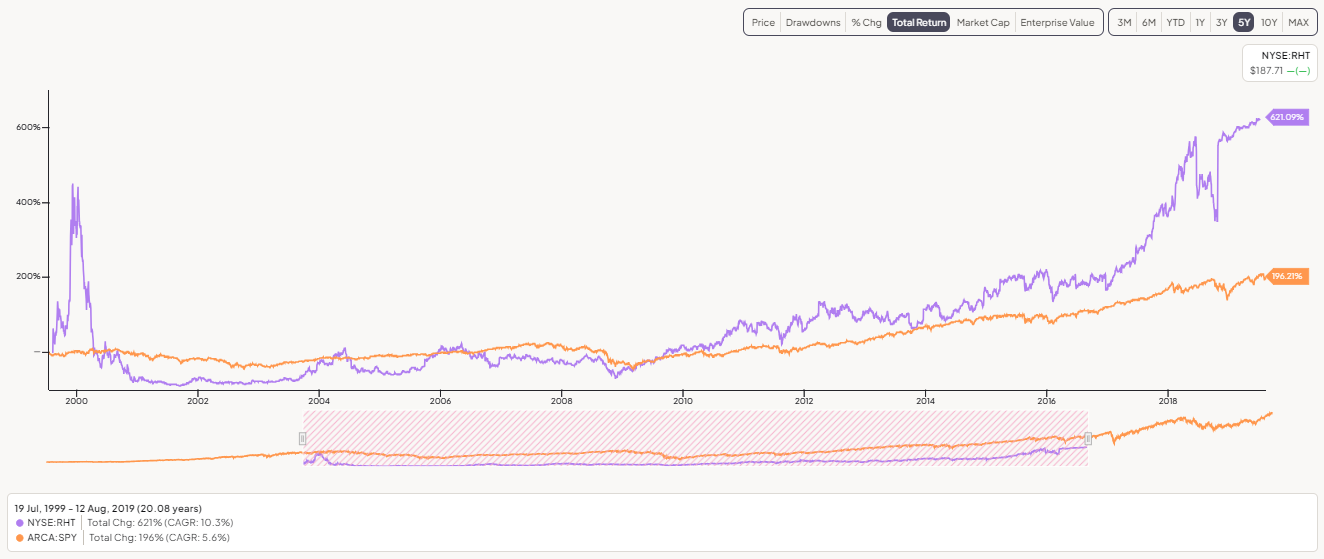
Red Hat became a public company in August 1999. Since then, it has generated a total return of 621% at a 10.4% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) over 19 years, outperforming the S&P 500. On October 28, 2018, IBM announced its intent to acquire Red Hat for $34 billion. The acquisition closed on July 9, 2019, and Red Hat now operates as an independent subsidiary.
The Key Takeaway
Red Hat has been successful due to its open-source products, low cost of entry, and affordable subscription fees. As an enterprise software company, Red Hat offers Linux products certified against government and other standards. No other companies provide a similarly powerful and certified Linux product in the market, so IBM was prepared to pay $34 billion to acquire Red Hat, acknowledging its exceptional and invaluable position in the industry.
MongoDB
MongoDB (Nasdaq: MDB) is an open-source database management program. The company began using open-source development in 2009 and introduced MongoDB as an open-source database server in 2010.
MongoDB is a NoSQL (Not only SQL) database, which is an alternative to traditional relational databases that’s useful for working with large amounts of distributed data. MongoDB is free and cross-platform, with two versions: Community and Enterprise. The Community version is free to download and use, but you can’t make changes to the source code. The Enterprise version has a license you need to pay for and includes additional security features, an in-memory storage engine, administration, authentication features, and monitoring capabilities. They also changed the license type for the enterprise version in November 2018.
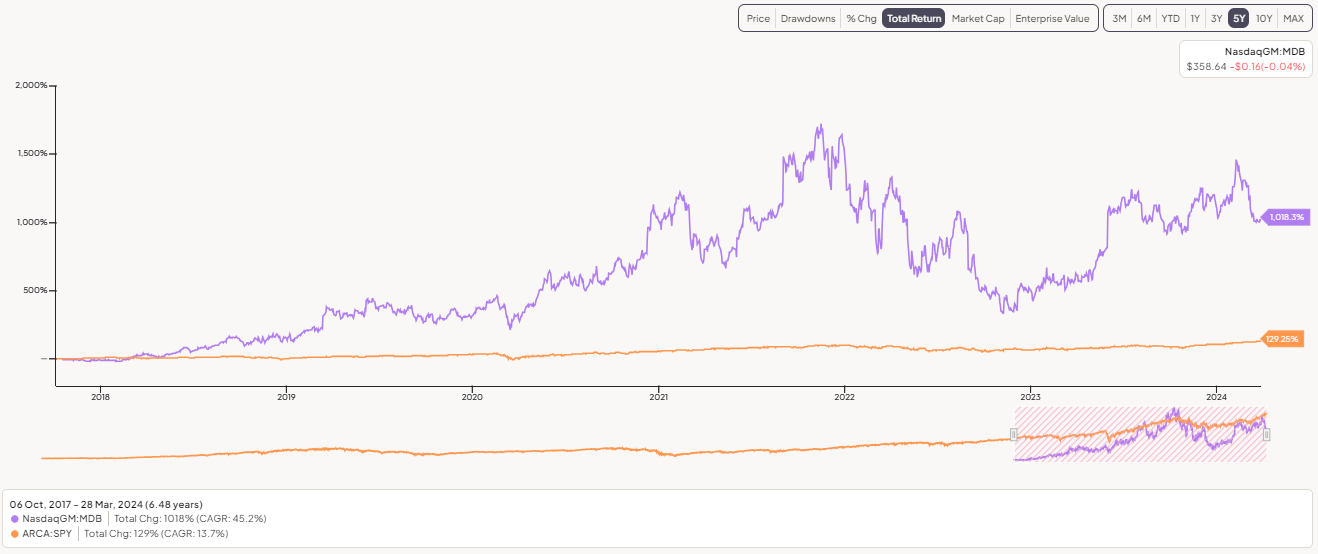
MongoDB listed its stock on the Nasdaq under the symbol MDB on October 19, 2017. MongoDB priced its initial public offering at $24 a share. Shares opened at $33 apiece and closed at $32.07.
Based on the recent quarter result, Atlas, MongoDB’s managed cloud database product that can run on the top three public cloud platforms, grew revenue by 34% in the fourth quarter and accounted for just over two-thirds of total revenue. Atlas customers reached 46,300 at the end of the quarter, up about 18% year over year.
The company has not been GAAP profitable, but growth has been fantastic. For fiscal 2025, MongoDB expects revenue to grow by just 14% to a range of $1.90 billion to $1.93 billion. That’s below the $2.04 billion expected by analysts. The company also expects adjusted earnings per share to be $2.27 to $2.49, down from $3.33 in fiscal 2024.
The stock is currently trading near $350 per share. It generated over 10x return in less than 5 years, beating the S&P500 nicely. It has had an incredible performance, and investors are pleased with it.
The Key Takeaway
MongoDB is more than just a database; it’s a comprehensive developer data platform. MongoDB’s success as a NoSQL data platform can be attributed to its developer-friendly nature, flexible document model, and ability to horizontally scale to support large volumes of data.
MongoDB Atlas stands out as the only globally distributed, multi-cloud database. With its scale-out architecture, MongoDB can efficiently manage numerous transactions and high data traffic volumes. Its robustness makes it stand out in the market, which is why MongoDB investors are enthusiastic and reaping significant rewards.
Confluent
The third company is still tiny but has characteristics similar to RedHat and MongoDB.
Confluent’s (Nasdaq: CFLT) Kafka is available as an open-source platform under the Confluent Community License, which allows users to download, modify, and redistribute code. However, the Confluent Community License is not open source and has some restrictions. For example, the license prohibits making available any software-as-a-service, platform-as-a-service, or other similar online service that competes with Confluent products.
The Confluent Platform is a data streaming platform that allows users to access, store, and manage data as real-time streams. It’s built by the original creators of Apache Kafka, the most popular open-source distributed streaming platform.
Confluent became public and launched its initial public offering on June 28, 2021, with $36 per share. It is still considered a newbie and in the public company. Based on the recent quarter, Q4 2023,
- Revenue of $213.184 million in Q4 2023, showing continued growth.
- A strong gross profit ratio of 0.732 in Q4 2023 indicates efficient cost management.
- The free cash flow of $14.299 million in Q4 2023 reflects operational efficiency.
The company is building strategic partnerships and leadership in the data streaming market. It collaborates with AI leaders and positions itself as a preferred provider for large language model stream processing. Because of the challenging macroeconomic environment, investors may be concerned about the valuation.
However, the company is well-positioned to capture the data streaming market. In a world of chatGPT and humanoids, data streaming is essential, not optional.
The Key Takeaway
Confluent is considered successful because it offers a cloud-native Kafka service that provides reliability, durability, scalability, and security. Confluent has managed over 30,000 Apache Kafka clusters and provides a 99.99% uptime availability SLA. Additionally, Confluent proactively detects data integrity issues with durability checks on over 80 trillion Kafka messages per day. Confluent Cloud is 10 times more elastic and offers faster scaling than Apache Kafka. Building a similar system in-house is exceptionally challenging and expensive, which is why Confluent is winning, and patient investors will be rewarded.




